AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun
Looking for the best AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun? Join CAD Centre Dehradun, the top-rated institute offering job-oriented AutoCAD Mechanical training with real-time projects, expert faculty, and 100% placement assistance.
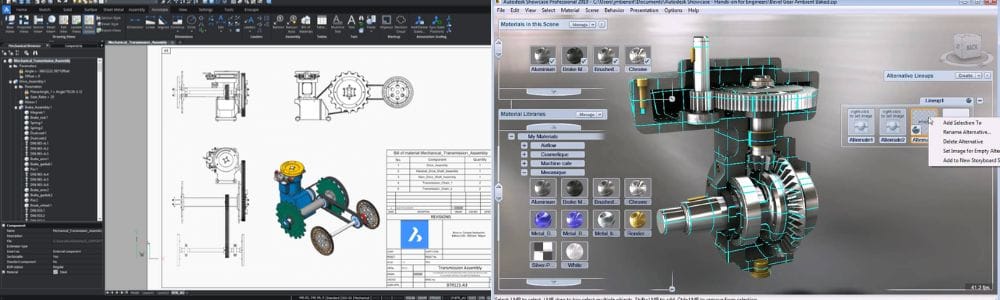
Why Choose AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun?
AutoCAD Mechanical is a vital tool for mechanical engineers and designers. At CAD Centre Dehradun, our AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun is designed to give you hands-on experience in 2D drafting, 3D modeling, and mechanical design principles used across industries.
Whether you’re a student or working professional, this course will help you gain the practical skills needed to excel in the manufacturing and mechanical design sectors.
Course Highlights:
✅ Industry-focused AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun
✅ Training by certified and experienced CAD professionals
✅ Modules include 2D Drafting, 3D Modeling, BOM Generation & GD&T
✅ Live projects & assignments
✅ Flexible batches – Weekend & Weekday
✅ Affordable fees with installment options
✅ CAD Certification after course completion
✅ Free career counseling and resume-building sessions
Software Training Modules – What You Will Learn
🔧 Core Modules:
Introduction to AutoCAD Mechanical Interface
Drawing and Editing Mechanical Components
Layer Management and Object Properties
Dimensioning & Tolerances (GD&T)
Bill of Materials (BOM) Creation
Mechanical Annotation Tools
Standard Parts Libraries
Advanced 2D Drafting Techniques
3D Modeling Basics (for Mechanical Elements)
Plotting & Printing Drawings
Real-time Project Design Simulations
🛠️ Additional Tools & Software Covered:
AutoCAD 2D & 3D (Mechanical Focused)
SolidWorks – Basic Overview for comparison
Fusion 360 – Industry Trends & Future Scope
Introduction to Creo & CATIA (overview sessions)
Placement Support:
Our AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun is backed by strong placement support. CAD Centre Dehradun has tie-ups with multiple design and manufacturing firms. We help our students get placed in companies across Dehradun and nearby industrial areas. Resume preparation, mock interviews, and job referrals are part of our placement cell’s support system.
Who Can Join?
Diploma/Engineering Students (Mechanical, Civil, Production)
Working professionals seeking CAD upskilling
Industrial designers
Job seekers aiming for design-based roles
Contact Us
-
9d Astley Hall, Dehradun, Above Book World, Dehradun, Uttarakhand 248001
- Sudhowala Chowk, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, 248007
- +91 7351229999
- info@reeaait.com
Student Reviews
FAQs
AutoCAD Mechanical is a specialized version of AutoCAD tailored for mechanical engineering design. It includes libraries of standard parts, tools for mechanical documentation, and features like GD&T symbols, BOM creation, and 2D drafting automation. By joining AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun at CAD Centre Dehradun, you gain industry-ready skills through expert-led classes, live projects, and placement support, helping you secure jobs in core engineering sectors.
The training typically lasts 45 to 60 days, depending on the batch type (Regular/Weekend/Fast-Track). The course fee for AutoCAD Mechanical Training in Dehradun at CAD Centre Dehradun is affordable and ranges between ₹8,000 to ₹12,000, with easy installment options available. Discounts may apply for early registration or group enrollment.
Yes, 100% placement assistance is offered. CAD Centre Dehradun has tie-ups with multiple industries and design firms across Uttarakhand. Students receive help with resume building, mock interviews, and direct job referrals after completing the course. Many alumni are now working as CAD designers and mechanical drafters in top companies.
This course is ideal for:
Mechanical & Production Engineering Students
Diploma holders in Mechanical, Civil, or Automotive fields
ITI students in drafting and design trades
Working professionals aiming to upgrade their design skills
Job seekers interested in CAD-based roles
.
The course covers:
Advanced 2D drafting & annotations
BOM generation & editing
GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing)
Use of standard parts & symbol libraries
Mechanical dimensioning techniques
3D view concepts
Project-based drawing creation for real-world applications
Yes, after successful completion, you will receive an industry-recognized CAD certification from CAD Centre Dehradun, which enhances your employability and adds credibility to your engineering resume.
Yes! CAD Centre Dehradun offers online AutoCAD Mechanical Training as well with live instructor-led sessions, recorded materials, and doubt-clearing classes. Online students also receive placement support and certification.
Absolutely. You can attend a free demo class at CAD Centre Dehradun to understand the teaching methodology, course structure, and interact with the faculty before enrolling.

